Depression affects countless individuals. According to Johns Hopkins Medicine, 9.5% of American adults will experience a depressive illness every year. Depression is more than just feeling sad occasionally — it’s a mental health disorder that can be so severe that it impacts one’s ability to enjoy everyday activities or function as they normally would. It can take a significant toll on overall well-being.
Many factors are involved in depression and there’s a significant link between nutrition and mental health. What your clients are putting in their bodies every day may be helping or harming their mental health.
No individual nutrient can cause or reverse depression. Helping your clients examine and optimize their overall diet is one of the best tools you can provide. Our brains thrive on foods that provide vitamins, minerals, fiber, protein, and healthy fats, which help support our mood.
Good nutrition is crucial to mental health. In fact, one 2017 study called the SMILES Trial found that when people with moderate-to-severe depression received nutrition counseling and ate a healthier diet for 12 weeks, their symptoms improved. As a practitioner, you can build client meal plans using The Clean Life that include foods that help with depression.
Key Nutrients & Foods in Meal Planning for Depression
Let’s unpack the nutrients and foods that help with depression that you can incorporate into your clients' plans.
Protein
Protein and amino acids are essential for muscle and tissue growth and repair, but they also appear to be especially important for people with depression. For example, our bodies use an amino acid called tryptophan to produce serotonin, an important brain chemical often called the “feel-good” hormone.
Serotonin is heavily involved in mood regulation and sleep, and there’s some evidence that it plays a role in depression as well. While the mechanism isn’t well understood, eating foods that help support serotonin production may benefit your clients.
Some of the best protein sources to incorporate into your clients’ meal plans include lean poultry, fish, legumes (beans, peas, and lentils), soy foods (tofu, tempeh, and edamame), nuts, and seeds.

Selenium
Selenium is a mineral that might help improve mood and reduce feelings of anxiousness. As many people who experience depression also struggle with anxiety, having adequate selenium in the diet may help make symptoms more manageable.
Selenium-rich foods include Brazil nuts, salmon, sardines, poultry, egg yolks, pumpkin seeds, chia seeds, garlic, onions, spinach, and dairy products.
Tip: Use That Clean Life’s free Nutrition Assessment Tool to collect the right information like your client's favorite foods, the amount of time they have to meal prep, and their cooking appliances so you can build great nutrition plans.
Zinc
Some studies have suggested that zinc levels may be lower among people with depression. While zinc supplementation is most often associated with helping you fight off cold symptoms, getting more zinc may also help antidepressants work more effectively.
Encourage your clients with depression to consume more food sources of zinc like beans, quinoa, zinc-fortified breakfast cereals, egg yolks, chicken, turkey, beef, pumpkin seeds, and garlic.
Tip: Use That Clean Life's filters to easily find recipes with zinc-rich foods like this Sauteed Chickpea & Edamame Bowl recipe.

B Vitamins
There are eight total B vitamins, but B12 and B9 (folate) may be particularly helpful in mental health.
These two vitamins may help protect and maintain the health of your nervous system. Some evidence suggests that having enough B12 and B9 available may help improve symptoms of mood disorders like depression.
Incorporate plenty of foods that provide B vitamins in your clients’ meal plans, such as salmon, beef, pork, dairy products, dark leafy greens (spinach, kale, lettuce, Swiss chard), Brussels sprouts, oranges, broccoli, and cauliflower.
Tip: Using That Clean Life, you can filter for nutrients like protein, selenium, zinc, vitamin B12, and folate.
That Clean Life offers a range of ready-to-use templates to help you create a comprehensive, evidence-based meal plan for your clients. Check out our Depression Support Diet and Plant-Based Depression Support Diet.
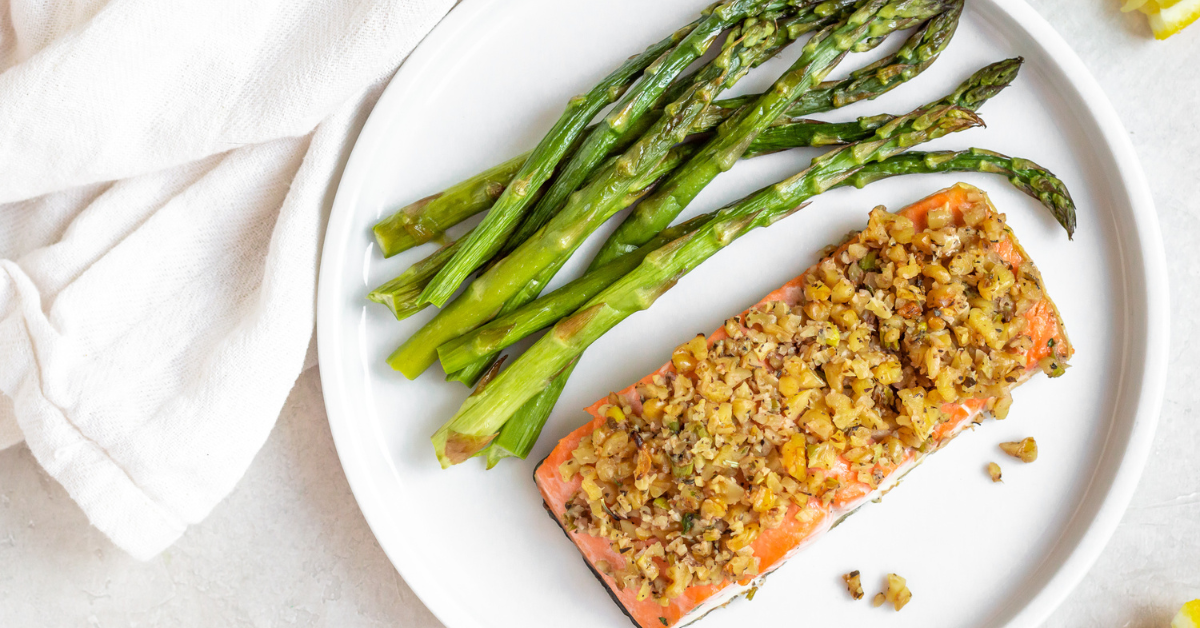
Omega-3 fatty acids
The omega-3 fatty acids include EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid), DHA (docosahexaenoic acid), and their precursor ALA (alpha-linolenic acid). It’s important to get direct sources of all three because the conversion rate of ALA to the other two is very low.
Omega-3 fatty acids play an important role in brain health and function, including neurotransmitter regulation and managing inflammation, which are linked to depression.
Dietary sources of omega-3s include fatty fish (salmon, halibut, mackerel, tuna), walnuts, eggs, chia seeds, and flax seeds.

Antioxidants
Antioxidants help protect your cellular health from damage that can promote disease.
A 2012 study suggested that including vitamins that act as antioxidants in your diet might help reduce anxiety symptoms among people with generalized anxiety disorder. This may also benefit individuals struggling with depression.
The best places to find antioxidants are colorful fruits and vegetables, like apples, citrus fruits, berries, cruciferous vegetables, dark leafy greens, sweet potatoes, tomatoes, avocados, carrots, and bell peppers.
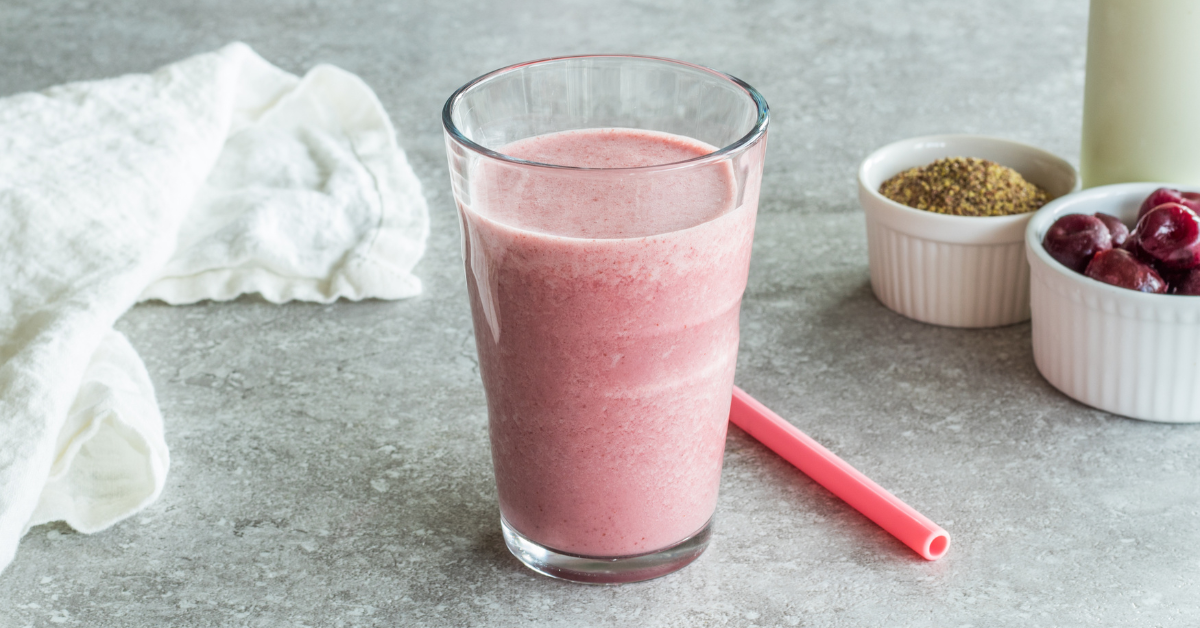
Probiotics
Maintaining a healthy gut microbiome refers to the trillions of microbes (bacteria, yeast, and fungi) living throughout your digestive tract. Research continues to show that having a healthy gut microbiome is essential for supporting the health of the rest of your body. For instance, a healthy gut microbiome may help reduce the symptoms and risk of depression.
Fermented foods are natural sources of probiotics, which can help promote a healthy balance of gut bacteria in your microbiome.
Include fermented foods like these in your clients’ meal plans for depression, like tempeh, miso, sauerkraut, kimchi, and kefir.
Tip: You can use the ingredients filter to find foods rich in omega-3s, antioxidants, and probiotics like this Cherry Kefir Smoothie.

Foods to Avoid
While you’re helping your clients eat more foods that help with depression, it’s equally important to help them ditch some that have the opposite effect.
For instance, many refined and ultra-processed foods that make up much of the Western diet pattern lack brain-healthy nutrients. These foods contribute calories without many vitamins, minerals, fiber, or antioxidants. Instead, they’re often high in saturated fat, added sugar, and sodium.
These types of foods are often enjoyed because they provide comfort in the moment and satisfy cravings. However, eating them in excess can increase the risk of many health problems, including depression.
Tip: You can use That Clean Life's "unprocessed" filter to find suitable recipes.
Key Lifestyle Considerations for Depression
Caring for our mental health requires a comprehensive lifestyle approach, including nutrition and other habits. When discussing nutrition and mental health with your clients, bring their attention to additional habits that can support their mood.
- Exercise: Regular movement boosts the production of endorphins, which are natural mood lifters. It also reduces levels of stress hormones like cortisol, which helps improve mood. Plus, exercising in ways we enjoy can increase self-esteem, social interaction, and feelings of accomplishment, all of which are good for mental health.
- Hydration: The brain works best when it’s adequately hydrated. Hydration also helps support neurotransmitter production and regulation, which can benefit mood. Encourage your clients to always keep a reusable water bottle with them to sip throughout the day.
- Sleep: Experts recommend adults get seven to nine hours of high-quality sleep each night. Being well-rested is essential for mood regulation and emotional well-being. It can also help manage symptoms of depression by promoting neuroplasticity, or the ability of our brains to rewire and grow.
- Therapy: Therapy provides a safe and supportive environment for clients to explore their thoughts, emotions, and experiences. Evidence-based therapeutic techniques can help people learn healthier coping strategies and skills to manage depressive symptoms.
- Medications: Antidepressants work by restoring the balance of brain chemicals. When used in conjunction with therapy and other lifestyle habits, medications can be effective for improving depressive symptoms.
Tip: Use the "drink" or "smoothie" filter on That Clean Life to find fun and hydrating recipes to help your clients reach their daily fluid needs.

Nourishing the Body and Mind
Nutrition is becoming more integrated into mental health counseling and we’re here for it. Equipping your clients with a nutrition plan to accompany their therapy and medications can make a huge difference in managing depressive symptoms. Helping them make daily choices that optimize their nutrition can benefit their physical and mental health.
Ready to create your depression support meal plan? Get started with That Clean Life’s ready-to-use Depression Support Diet and Plant-Based Depression Support Diet.
Each plan includes a 7-day meal plan, an itemized shopping list, appropriate recipes, a prep guide, and supporting evidence. The programs are fully customizable based on your client’s needs and preferences.
If you are not yet a member of That Clean Life, watch our demo here to see how it works!

